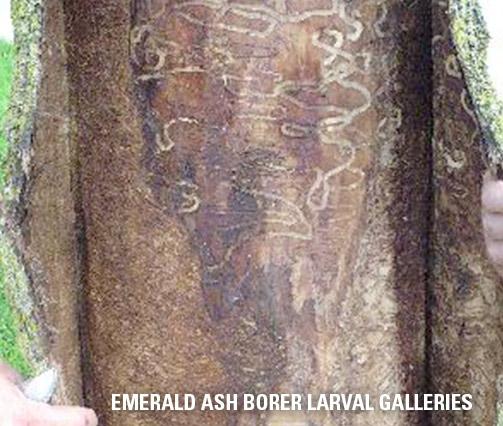Emerald Ash Borer
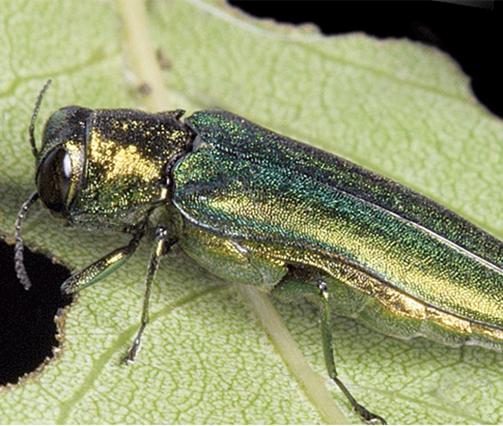
The Emerald Ash Borer (EAB, Agrilus planipennis) is an invasive pest introduced from Asia that attacks and kills most ash trees species.
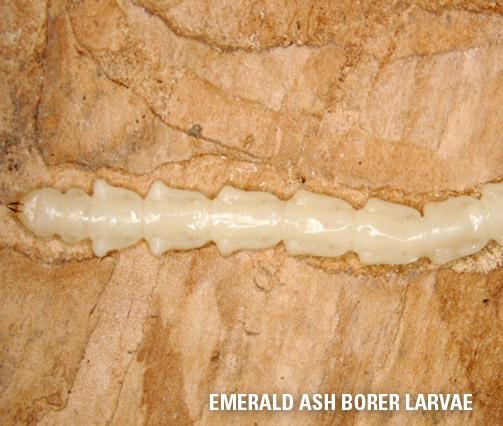
This metallic wood boring beetle was found in Detroit, Michigan and Ontario, Canada in 2002, and has continued to spread into neighboring states and eventually across the U.S. and Canada. The adult is a small, metallic green beetle only 10-15 mm in length and about 3 mm in width. The larvae live under the bark of the tree and feed in the vascular cambium. The adults typically emerge around June, leaving D-shaped exit holes in the bark. The adult beetle will briefly feed in the canopy before laying eggs in the twigs and branches.
Common Symptoms
EAB larvae live under the bark and feed on the vascular tissues. Larvae create meandering galleries through the phloem, vascular cambium and etch the xylem, effectively girdling the tree. Dieback of the canopy is a symptom of EAB larval infestation; many of the branches may die back as infestation progresses. The tree responds by sprouting new (epicormic) branches below the disrupted tissues. The bark will split over dead vascular tissues, and trees may die within two years of the onset of symptoms.
Treatments
Independent studies strongly recommend that treatments be applied early, before extensive disruption to the vascular tissues occurs. Dieback symptoms should be <40%. Arborjet recommends treatment when EAB is detected in your area, but trees still appear healthy for best outcomes. Treat ash with either TREE-äge® G4 or R10 Insecticide (emamectin benzoate), IMA-jet® or IMA-jet 10 (imidacloprid) or AzaSol® using the TREE I.V. system for high volume dosages or the QUIK-jet® or QUIK-jet Air® micro-injector for lower volume applications. TREE-äge, IMA-jet, and AzaSol will kill the EAB larvae inside the tree.
See the TREE-äge, IMA-jet, and AzaSol labels for dosage rate based on tree size.
To give the tree a greater health benefit, a follow-up application of Mn-jet Fe® or NutriRoot® is recommended, the specific formulation dependent upon soil type. When applied to the soil, NutriRoot, will supply phosphorous, potassium, iron, manganese, humectants, humic acid and a low dose of nitrogen for healthy leaf and root development. Mn-jet Fe supplies both iron and manganese, micro-elements that may be sequestered in high pH soils, but essential to healthy, green foliage.
When To Treat
Treat ash if EAB is reported within 30 miles of your area. Do not wait for visible dieback in the canopy, as there is a significant delay between disruption to the vascular tissues and expression of symptoms in the canopy. Delaying Emerald Ash Borer treatment could result in canopy dieback or tree loss. Applications should be made in the spring, about 30 days prior to expected adult emergence; however, treatment may be applied during the growing season (May – September) to protect trees. Uptake of formulation is fastest when trees are actively transpiring after they have developed a full canopy. Emerald Ash Borer treatment in the spring will prevent the adult beetles from feeding and laying eggs in the tree, whereas summer treatment will kill the larval stage of EAB feeding under the bark. Make summer treatment applications in the morning when temperatures are moderate. If soil is dry, water trees prior to treatment. Injection in the fall (after leaves color) can protect the tree for the following season.
Trees need to be closely monitored for symptoms of EAB as infestation builds in your area. In general, applications are not made more than once a year. TREE-äge treatments for EAB provide 2 years of activity.
What To Expect After Treatment
TREE-äge will kill the EAB larvae under the bark as well as adult beetles that feed on the tree. IMA-jet will also kill the EAB larvae under the bark and deter adult feeding on the treated tree. TREE-äge will provide 2 years residual control. The long-term prognosis for trees that are treated early (i.e., before vascular injury) is very good to excellent. Tree recovery from an established infestation is relative to the severity of the infestation at the time of treatment. A single application of IMA-jet will provide control of EAB for a full year.
References And Photo Credits
Main Photo of adult EAB by Dave Cappaert, Michigan State University, Bugwood.org
Larvae taken by Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources – Forestry Archive, Bugwood.org
Bark Damage taken by Joseph O’Brien, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Canopy Damage taken by Arborjet, Inc